The Giger MD therapy
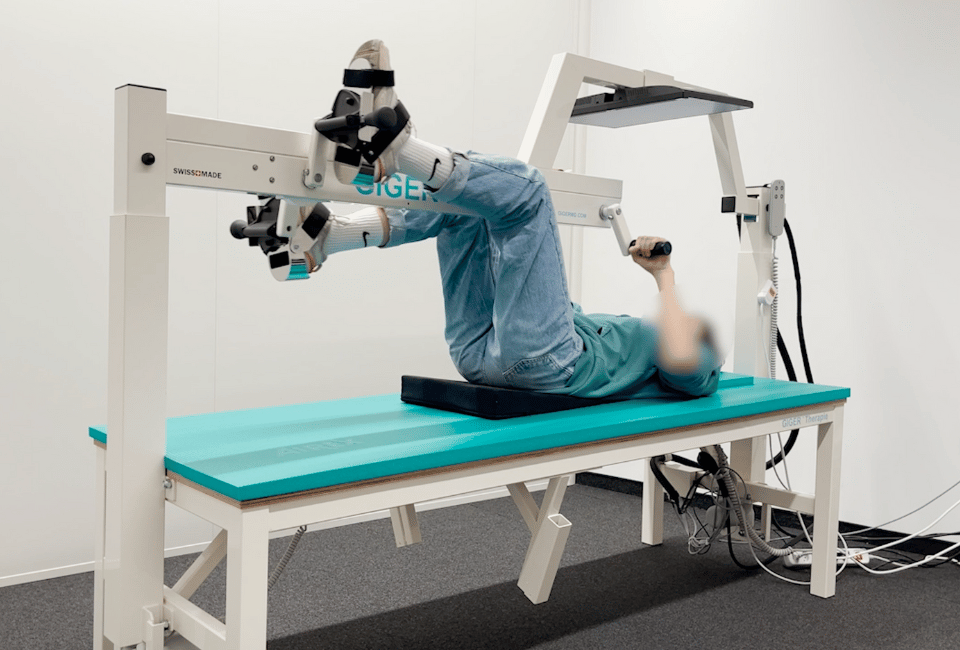
New and exclusive to our center, the Giger MD device is a complementary treatment to the Tomatis method for attention deficit, dyslexia and language disorders. Let's see how & why.
Read the following testimonial from a teacher at the end of Clara's 2nd quarter:
"She is getting very good averages in all subjects and her progress is impressive! We congratulate her on her results and the dedication she has shown this term in all areas. Clara seems to have gained confidence. She is actively participating in all lessons, asking questions, and seeking out the adult when she needs it."
The Giger MD therapy
The Giger MD therapy is designed to help improve the coordination and organization of different sensorial and motor inputs in the central nervous system (CNS) by using biofeedback technology. The therapy is based on the idea that the coordination of the firing of neurons in the CNS is crucial for the self-organization of the CNS, and that this coordination can be partially lost after an injury or disease. The therapy utilizes high-tech instruments to help patients relearn precise and coordinated movements, by coordinating the phase and frequency of the movements down to a few milliseconds, which can help to restore the basic structure of the CNS.
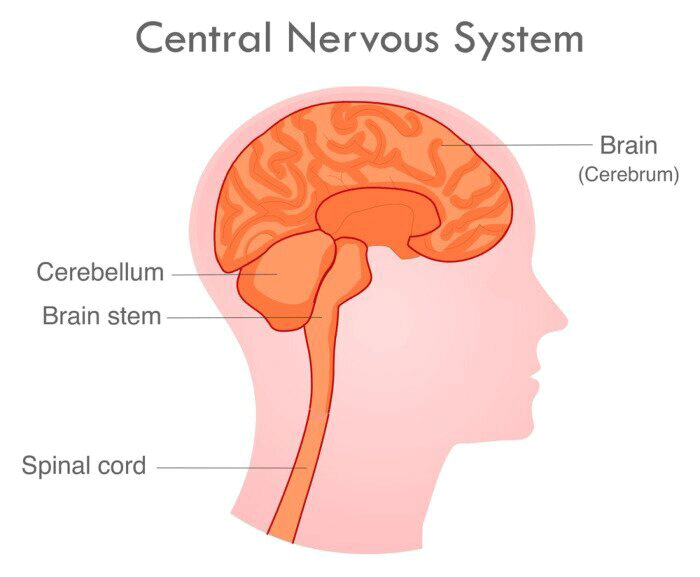
If the CNS is not functioning properly, it can have difficulty processing and integrating different sensorial and motor inputs, which can lead to problems with attention. By improving the coordination and organization of different sensorial and motor inputs in the CNS, the Giger MD therapy can help to improve the overall functioning of the CNS, which can in turn improve attention.
It's worth noting again that the therapy is primarily used to help individuals with movement disorders and it is not a direct treatment for cognitive functions like attention, but by addressing the underlying movement disorder, the therapy may improve overall cognitive function and improve attention as a secondary benefit.
The rule of Hebb
The rule is often described as "cells that fire together, wire together." It suggests that the connection between two neurons (called a synapse) becomes stronger when those neurons are activated at the same time. The idea is that the more often the neurons are activated together, the stronger the connection becomes.
The rule of Hebb is thought to play a role in the formation of memories and the strengthening of neural connections in the brain. It is based on the idea that the brain is constantly rewiring itself in response to experiences, and that the connections between neurons are modified based on their activity patterns.
Overall, the rule of Hebb is a fundamental principle in neuroscience that helps to explain how the brain changes and adapts in response to experiences. It is a key concept in the study of learning and memory, and has been widely researched and debated by scientists for many years.
Why the CNS and attention are related
The central nervous system (CNS) is made up of the brain and the spinal cord, and it is responsible for controlling and coordinating the body's functions, including attention. Attention is the ability to focus on a specific task or source of information while disregarding others. It is a cognitive process that is controlled and coordinated by various regions of the brain.
Several regions of the brain are involved in attention, including the prefrontal cortex, parietal cortex, and the thalamus. The prefrontal cortex is responsible for executive functions, such as planning, decision making, and impulse control, which are all important for attention. The parietal cortex is responsible for spatial attention, which is the ability to focus on a specific location or object in the environment. The thalamus acts as a relay station between the senses and the cerebral cortex, and it plays a role in filtering and directing incoming sensory information to the appropriate brain regions.
The CNS also plays a role in regulating the release of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals between neurons in the brain. These neurotransmitters play an important role in attention by regulating the activity of the neurons involved in attentional processes. For example, dopamine, which is involved in motivation and reward, can also help improve attention and focus.
Attention disorders, such as ADHD, are thought to be related to abnormal function of the CNS, specifically in the regions of the brain that are responsible for attentional processes. Research suggests that attention disorders may be associated with imbalances in neurotransmitters, abnormal development of certain brain regions, or exposure to certain environmental toxins.
In conclusion, the central nervous system, specifically the brain, plays a crucial role in regulating attention. The brain regions and neurotransmitters involved in attention are closely related and work together to help us focus and filter out distractions. Attention disorders may be related to abnormal function of the CNS, which can be treated with a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes.
How the Giger MD works
The Giger MD therapy is based on five main principles:
- The CNS is considered a neural network that can be changed through relearning.
- The coordination of the firing of neurons is the basis for the self-organization of the CNS.
- Learning processes stimulate and control the formation of new nerve cells, including coordinated rhythmic movements.
- Through relearning, the functions of the CNS can be significantly improved.
- The CNS has the ability to integrate, store, and retrieve different network states, which can be used to reorganize an impaired or injured CNS
The therapy is based on the use of high-tech therapy instruments that help patients to relearn precise and coordinated movements. These instruments are designed to coordinate the phase and frequency of the movements down to a few milliseconds, which can help to restore the basic structure of the CNS.
The therapy is typically administered for a period of 3 to 6 months, and we have reported to have significant improvement on patients with coordination issues, speech and language disorders, dyslexia, ADD or ADHD.
You can also find an article about our GIGER MD program to reduce stuttering.



